Introduction to TDD
What is Test Driven Development?
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development process or practice in which the developer starts by writing tests for their code based on the requirements instead of writing the implementation code itself directly. The main reason behind doing so is to let the requirements drive the code. This has the added advantage that we write testable code out of the box which tends to me cleaner and more maintainable.
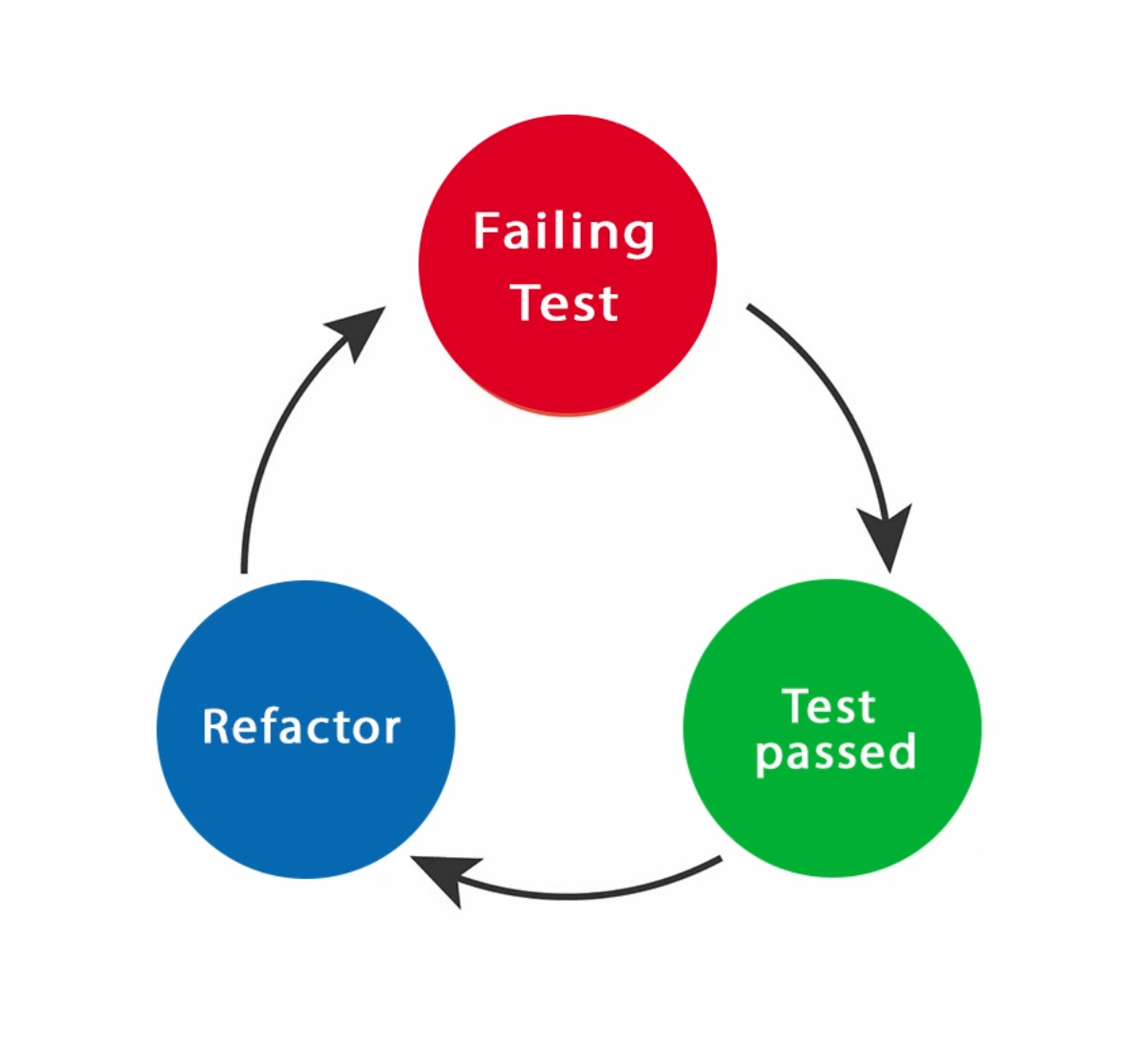
TDD has 3 main phases/steps that form a continuous loop:
- Red
- Green
- Refactor
Red
This is the first phase. The developer starts by writing a test that they know will fail because they don't have the implemented code for that test. The code has to compile because the red test needs to be run, but the developer will go only far as creating the class or method needed for the test to run.
Green
This is the second phase. The developer will now implement the minimum amount of code to make this test pass. It doesn't have to be amazing code. It just needs to make the test pass, or make it Green. Focusing too much time to making the "perfect" implementation out of the box, is a mistake. We simply want to write enough code for the test to pass and use that as a "harness" or a safety net to know that we can make this test pass.
Refactor
This is the third phase. The developer will now refactor the code that made that test green. Remember, the point wasn't to write perfect code the first time around. It was to make that test pass to ensure that our use-case is satisfied. Now you can write the best code you can, knowing that your test was green.
This is how the process can be visualized:
But why?
It's very simple. You eradicate the fear of change. You can guarantee from the beginning that your code is covered so when something changes or is added, you will know if any of the previous code was affected because there will be a test that goes red. When that test goes red, it's up to you to go through the cycle again and make it Green and then refactor it.